ABOUT CYPRUS
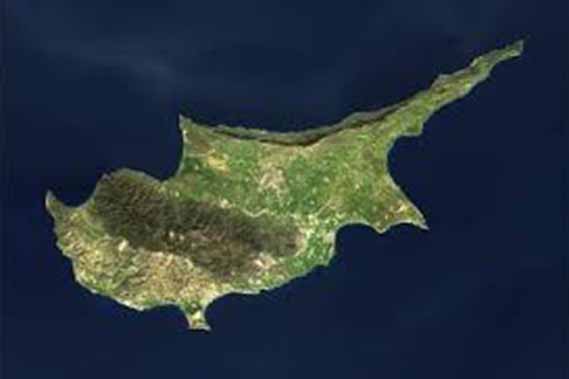
GEOGRAPHY
Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia, with an area of 9.251 sq. kms (3.572 sq. miles).
It is situated at the north-eastern corner of the Mediterranean, at a distance of 300 km north of Egypt. The Greek island of Rhodes lies 360 km to the north-west.
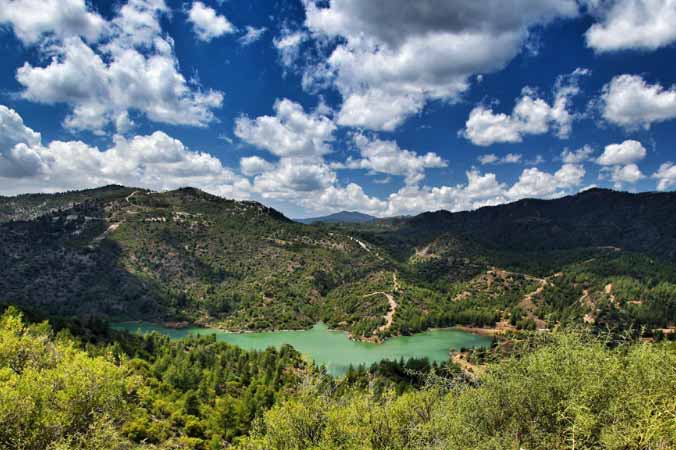
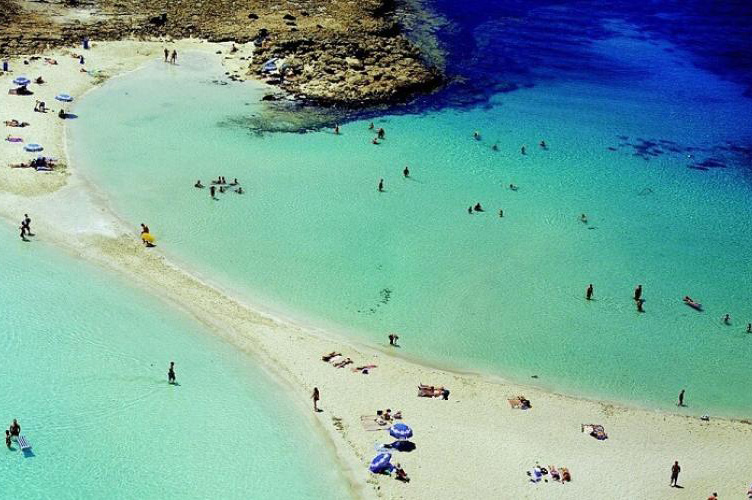
Cyprus’ coastal line is indented and rocky in the north with long sandy beaches in the south. The north coastal plain, covered with olive and carob trees, is backed by the steep and narrow Pentadaktylos mountain range of limestone, rising to a height of 1.042 m. In the south, the extensive mountain massif of Troodos, covered with pine, dwarf oak, cypress and cedar, culminates in the peak of Mount Olympus, 1.953 m. above sea level. Between the Troodos range and the Pentadaktylos mountain range lies the fertile plain of Messaoria.

DEMOGRAPHY
The population of the Republic of Cyprus is 938.400 (2014) of whom 694.700 belong to the Greek Cypriot community, (74%), 91.400 (9,8%) to the Turkish Cypriot community (estimate) and 152.300 (16,2%) are foreign citizens residing in Cyprus. The language of the Greek Cypriot community is Greek and the community adheres predominantly to the Autocephalous Greek Orthodox Church of Cyprus. The language of the Turkish Cypriot community is Turkish and the members of the community are Sunni Muslims.

HISTORY
The history of Cyprus is one of the oldest recorded in the world and its historical significance is disproportionate to its small size. The first signs of civilisation date to the ninth millennium B.C. The earliest known foreign settlements on the island were mainly of Phoenicians and Greeks, with Phoenician culture dominating the island’s eastern and southern parts. As a strategic location in the Middle East, it was subsequently occupied by several major powers, including the empires of the Assyrians, Egyptians, and Persians, from whom the island was seized in 333 BC by Alexander the Great and at which point Greek culture began to dominate. Subsequent rule by Ptolemaic Egypt, the Roman Empire, the Byzantines, Arab caliphates for a short period, the French Luisignan dynasty, and the Venetians, was followed by over three centuries of Ottoman control. Cyprus was placed under British administration in 1878 until it was granted independence in 1960.

CLIMATE
Cyprus has a Mediterranean climate: hot, dry summers from June to September and mild, wet winters from November to March, which are separated by short Autumn and Spring seasons. Sunshine is abundant during the whole year, particularly from April to September when the daily average exceeds eleven hours. Winds are on the whole light to moderate. Gales are very infrequent and heavy storms rare.
Snow hardly falls in the lowlands and on the northern range, but is a frequent feature, every winter on ground above 1.000 metres in the Troodos range. During the coldest months it lies in considerable depth for several weeks, attracting skiers.

FOOD & DRINK
Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia, with an area of 9.251 sq. kms (3.572 sq. miles).
The food of Cyprus reflects the rich and turbulent history of the island and its indelible Greek culture. You will find tastes influenced by the Middle East, Asia Minor and the Venetians, all using fresh local ingredients, herbs and spices and olive oil. The Mediterranean diet, with its grains and pulses, sun-ripened fresh fruit and vegetables, high-protein fish, lean meat and poultry and wine, is a healthy option.
Cyprus has a long tradition in winemaking that goes back over 4,000 years. In ancient times wine was a major source of wealth for the island. The island supplied the Pharaohs of Egypt and Cyprus wines were in great demand amongst the ancient Greeks and Romans.

FLAG OF CYPRUS
The flag of the Republic of Cyprus was defined in 1960 when Cyprus became an independent sovereign state.
The background is white with a copper-coloured (pantone 1385 C) silhouette of the map of Cyprus in the centre of the flag, above two crossed olive-green-coloured (pantone 574 C) olive branches. The copper colour has a dual symbolism: first, the name of the island is said to derive from an ancient word for copper (Eteocypriot or Sumerian); and second, copper is closely associated with Cyprus since antiquity when the island became a major producer and supplier of this mineral resource. The olive branches are symbols of peace.
